Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 with surface hydroxyl groups in lithium silicates
with surface hydroxyl groups in lithium silicatesNakazawa, Tetsuya; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Grismanovs, V.*; Katano, Yoshio*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part2), p.1436 - 1440, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.15(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Satoru; Sato, Haruo; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Fujii, Naoki*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
JNC TN8400 2001-031, 44 Pages, 2002/05
In order to quantify effect of temperature on diffusivity of deuterated water (HDO) in compacted sodium-bentonite, through-diffusion experiments were conducted at elevated tempemture from 298 to 333 K. Kunipia F (Na-montmorillonite content  98 wt. %; Kunimine Industly Co.) was compacted to a dry density of 0.9 and l.35 Mg/m
98 wt. %; Kunimine Industly Co.) was compacted to a dry density of 0.9 and l.35 Mg/m . Since smectite flakes were perpendicularly oriented to a direction of compaction, anisotropy of diffusivity was investigated parallel and normal to the preferred orientation of smectite. Effective diffusion coeficient D
. Since smectite flakes were perpendicularly oriented to a direction of compaction, anisotropy of diffusivity was investigated parallel and normal to the preferred orientation of smectite. Effective diffusion coeficient D of HDO was larger for a diffusional direction parallel to the preferred orientation than normal to that for both dry densities. These results well agreed to the previously reported ones for tritiated water. Activation energies of D
of HDO was larger for a diffusional direction parallel to the preferred orientation than normal to that for both dry densities. These results well agreed to the previously reported ones for tritiated water. Activation energies of D in compacted bentonite increased with increasing dry density in the range of 19 - 25 kJ/mol which was slightly larger than that in bulk water (18 kJ/mol). This relationship can be considered to be due to both the pore structure development and high activation energy of water (18-23 kJ/mol) in the vicinity of smectite surface (within 2 nm) on the basis of molecular dynamics simulations.
in compacted bentonite increased with increasing dry density in the range of 19 - 25 kJ/mol which was slightly larger than that in bulk water (18 kJ/mol). This relationship can be considered to be due to both the pore structure development and high activation energy of water (18-23 kJ/mol) in the vicinity of smectite surface (within 2 nm) on the basis of molecular dynamics simulations.
 O molecules from surface hydroxyl groups in silicates
O molecules from surface hydroxyl groups in silicatesNakazawa, Tetsuya; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Grismanovs, V.*; Katano, Yoshio*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 297(1), p.69 - 76, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Futakuchi, Katsuhito*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Sakuramoto, Yuji*; ;
JNC TN8400 2001-007, 52 Pages, 2001/04
As a natural analogue, the authors investigted a Tertiary argillaceous bed and a Quarternary hypabyssal rock (porphyrite) which intruded into the argillaceous rock, distributed in the Nishikubiki district of Niigata prefecture in Japan. We examined the variation of clay mineral species in the argillaceous rock surrounding the intrusive rock and carried out thermal analyses for the argillaceous rock based on the coolig history of the intrusive rock. The predominant clay mineral varied from montmorillonite to illite through illite/montmorillonite interlayers with approaching to the intrusive rock. The thermal analyses indicated that the temperature descended from 270 to 15  C during the 7.5
C during the 7.5 10
10 years at alocalty of argillaceous rock containing 75% illite in the interlayers. On the assumption that the alteration from montmorillonite to illite was regarded as a first-order reaction, we evaluated the apparent activation energy based on the thermal condition mentioned above; about 103 kJ/mol was obtained for this illitization. This was within the range of values reported previously by laboratory experiments and/or examinations of natural illitizations.
years at alocalty of argillaceous rock containing 75% illite in the interlayers. On the assumption that the alteration from montmorillonite to illite was regarded as a first-order reaction, we evaluated the apparent activation energy based on the thermal condition mentioned above; about 103 kJ/mol was obtained for this illitization. This was within the range of values reported previously by laboratory experiments and/or examinations of natural illitizations.
JNC TN8400 2001-008, 36 Pages, 2001/03
Research on geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste(HLW) has been underway in many countries. Bentonite exhibiting a low permeability, high swelling property and high sorption capacity for many radioelements is proposed as a buffer material in many countlies. Recently, cementitious materials are considered as candidate matelials for the geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste. As the pH and the Ca, Na, K contents of hyperalkaline pore water from the cementitious materials are high, this hyperalkaline pore water would alter the buffer material. The main aim of this study is to investigate the effect of alkaline pore water into the bentonite. Used materials are montmorillonite, albite and quartz composing bentonite. These minerals mixed in a constant ratio (1:1wt%) made to react to distilled water and the alkali solutions (pH11-13). These studies have been conducted at temperatures of 50 - 150 C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test
C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test  Montmorillonite test
Montmorillonite test  Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E
Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E ) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
Suzuki, Satoru; ; *
JNC TN8400 2000-020, 25 Pages, 2000/04
Nature of porewater in bentonite plays important roles on the mass transport in the compacted bentonite used as a physical and chemical buffer material of the multi-barrier system in the high level radioactive waste manegement Higher activation energies of diffusion in the compacted bentonite than those in the aqueous solution is due probably to change in molecular structure of water in the porewater. The Raman spectroscopy was applied to studying the structure of porewater in bentonite at room temperature. Bentonite (Kunipia F, 98-99wt% of Na-smectite) was mixed with ion-exchanged water by water content of 75, 80, 90, 95 and 98wt% of water or with 0.5M NaCl aqueous solution by 75 and 80wt% of NaCl solution. Intensity maxima of the spectra of ion exchanged water, NaCl solution and their porewater were observed near 3200 to 3250, 3400, 3630cm . These bands can be attributed to water molecules forming stronger hydrogen bond in this manner. Ratio of intensity, 3250cm
. These bands can be attributed to water molecules forming stronger hydrogen bond in this manner. Ratio of intensity, 3250cm /3400cm
/3400cm , increased from 0.97 to 1.1 with a decrease in water content of 100wt% (water) to 75wt%. On the other hand, intensity ratio of 3400cm
, increased from 0.97 to 1.1 with a decrease in water content of 100wt% (water) to 75wt%. On the other hand, intensity ratio of 3400cm /3250cm
/3250cm of NaCl aqueous solution, 80wt%and 75wt% were 0.92, 1.2 and 1.3, respectively. Since the Raman scattering near 3250cm
of NaCl aqueous solution, 80wt%and 75wt% were 0.92, 1.2 and 1.3, respectively. Since the Raman scattering near 3250cm was attributed to water molecule forming the strongest hydrogen bonding in the three bands, those changes in intensity ratio suggests an increase in number of water molecule forming strong hydrogen bond in porewater of the bentonite. The constrained porewater possibly results in the high activation energy of diffusion in the compacted bentonite.
was attributed to water molecule forming the strongest hydrogen bonding in the three bands, those changes in intensity ratio suggests an increase in number of water molecule forming strong hydrogen bond in porewater of the bentonite. The constrained porewater possibly results in the high activation energy of diffusion in the compacted bentonite.
*; *; *; *; Hasegawa, Makoto; Hirano, Koichiro
JNC TY9400 2000-007, 50 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Miyata, Teijiro*; Takada, Junichi; Ida, Masaaki*; Nakagiri, Naotaka*; Koike, Tadao; Tsukamoto, Michio; Watanabe, Koji*; Nishio, Gunji*
JAERI-Tech 2000-035, p.64 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-018, 79 Pages, 2000/02
As a basic research for geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes, diffusion behavior of radionuclides and corrosion behavior of overpack materials in clay buffer materials (bentonite) were studied. In the study on the diffusion behavior of radionuclides, basal spacing and water content were determined for water saturated, compacted Na-montmorillonite that is major clay mineral of bentonite. The apparent diffusion coefficients of Na , Sr
, Sr , Cs
, Cs and Cl
and Cl ions and their activation energies were also determined at different dry densities of montmorillonite. For all kinds of ions, the activation energies were found to increase as the dry density increased. These findings suggest that the diffusion mechanism of ions in compacted montmorillonite changed with increasing dry density. As a reasonable explanation for the changes in the activation energy, we proposed a multiprocess diffusion model, in which predominant diffusion process is considered to change from pore water diffusion to interlayer diffusion via surface diffusion when the dry density increases. The Na-montmorillonite is expected to alter by the ion exchange with Ca
ions and their activation energies were also determined at different dry densities of montmorillonite. For all kinds of ions, the activation energies were found to increase as the dry density increased. These findings suggest that the diffusion mechanism of ions in compacted montmorillonite changed with increasing dry density. As a reasonable explanation for the changes in the activation energy, we proposed a multiprocess diffusion model, in which predominant diffusion process is considered to change from pore water diffusion to interlayer diffusion via surface diffusion when the dry density increases. The Na-montmorillonite is expected to alter by the ion exchange with Ca ions, which could be introduced from groundwater and/or cementitious materials in a repository. The apparent diffusion coefficients of Na
ions, which could be introduced from groundwater and/or cementitious materials in a repository. The apparent diffusion coefficients of Na and Cs
and Cs ions and their activation energies were studied for Na/Ca montmorillonite mixtures in order to know the effect of this kind of alteration on the diffusion behavior of ions. It was found that the alteration of montmorillonite affected diffusion coefficients and the activation energies for both kinds of cations. These effects cannot be explained only by the pore water diffusion. The multiprocess diffusion model proposed in this study is suggested as the most reasonable explanation for the effects. The oxidation behavior of pyrite in bentonite during drying process was studied for understanding corrosion behavior of overpack materials in bentonite. There ...
ions and their activation energies were studied for Na/Ca montmorillonite mixtures in order to know the effect of this kind of alteration on the diffusion behavior of ions. It was found that the alteration of montmorillonite affected diffusion coefficients and the activation energies for both kinds of cations. These effects cannot be explained only by the pore water diffusion. The multiprocess diffusion model proposed in this study is suggested as the most reasonable explanation for the effects. The oxidation behavior of pyrite in bentonite during drying process was studied for understanding corrosion behavior of overpack materials in bentonite. There ...
Miyata, Teijiro; Takada, Junichi; Ida, Masaaki*; Nakagiri, Naotaka*; Tsukamoto, Michio; Koike, Tadao; *; Nishio, Gunji*
JAERI-Tech 99-039, 70 Pages, 1999/05
no abstracts in English
Morita, Yosuke; Yagi, Toshiaki; *
Denki Gakkai Yuden, Zetsuen Zairyo Kenkyukai Shiryo; DEI-99-13, p.27 - 30, 1999/02
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Tetsuaki; Iwatsuki, Jin*; Ogawa, Masuro
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-6-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu '98 Koen Rombunshu, p.90 - 95, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Okayasu, Satoru; *
Proc. of 9th Int. Symp. on Superconductivity, 0, p.507 - 510, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Okayasu, Satoru; *
Czechoslovak Journal of Physics, 46(SUPPL.S3), p.1645 - 1646, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Yagi, Toshiaki; Morita, Yosuke; Seguchi, Tadao; *
Denki Gakkai Yuden, Zetsuen Zairyo Kenkyukai Shiryo; DEI-94-90, 0, p.21 - 28, 1994/12
no abstracts in English
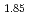 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO single crystal
single crystalOkayasu, Satoru; ; *; *
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 194-196, p.1881 - 1882, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.36(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
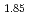 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO single crystal
single crystalOkayasu, Satoru; ; *; *
Superconductors, Surfaces and Superlattices (Trans. of Materials Research Soc. Jpn., Vol. 19A), 0, p.421 - 424, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Yagi, Toshiaki; Morita, Yosuke; Seguchi, Tadao
DEI-93-155, p.19 - 26, 1993/12
no abstracts in English